Psychometric and physiological responses to a pre-season competitive camp in the heat with a 6-hr time difference in elite soccer players
Buchheit, M., Cholley Y. and Lambert P. Psychometric and physiological responses to a pre-season competitive camp in the heat with a 6-hr time difference in elite soccer players. IJSPP, In press.
Purpose. The aim of the present study was to examine in elite soccer players some psychometric and physiological responses to a competitive camp in the heat, after travelling across 6 time-zones. Methods. Data from 12 elite professional players (24.6±5.3 yr) were analyzed. They participated in an 8-day pre-season summer training camp in Asia (heat index 34.9±2.4 ⁰C). Players’ activity was collected during all training sessions and the friendly game using 15-Hz GPS. Perceived training/playing load was estimated using session rate of perceived exertion (RPE) and training/match duration. Psychometric measures of wellness were collected upon awakening before, during and after the camp using simple questionnaires. HR response to a submaximal 4-min run (12 km/h) and the ratio between velocity and force load (accelerometer-derived measure, a marker of neuromuscular efficiency) response to 4 ~60-m runs (22-24 km/h) were collected before, at the end and after the camp. Results. After a large increase, the RPE/m.min-1 ratio decreased substantially throughout the camp. There were possible small increases in perceived fatigue and small decreases in subjective sleep quality on the 6th day. There were also likely moderate (~3%) decreases in HR response to the submaximal run, both at the end and after the camp, which were contemporary to possible small (~8%) and most-likely moderate (~19%) improvements in neuromuscular efficiency, respectively. Conclusions. Despite transient increases in fatigue and reduced subjective sleep quality by the end of the camp, these elite players showed clear signs of heat acclimatization, which were associated with improved cardiovascular fitness and neuromuscular running efficiency.
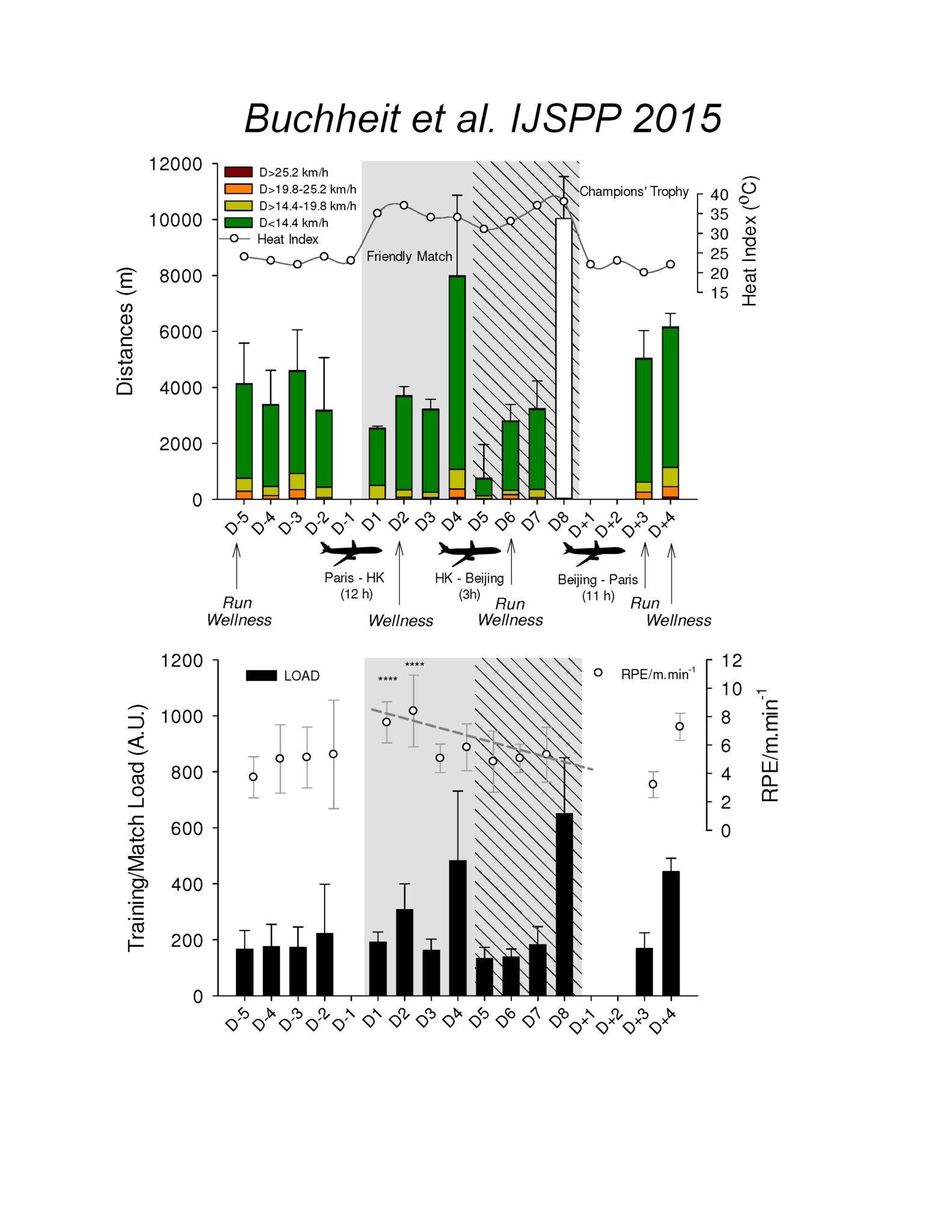
Figure 1. Upper panel: change in locomotor load (measured via GPS) and heat index before, during and after the Asian camp. The flights represent the different flying trips, with their specific duration indicated into brackets. As wearing GPS was not allowed during the official match, the total distance covered was extrapolated from historical club data (Team A) against Team B for illustration. The timing of the monitoring sessions is also indicated, with Run standing for the submaximal run and the 4 60-m runs, and Wellness for the psychometric questionnaires. Lower panel: changes in perceived training load (rate of perceived exertion, RPE, method) and the RPE/distance per min ratio. The gray area represents the Hong Kong (HK) camp, while the grey and shaded area represents the time spent in Beijing. ****: very likely different vs. pre camp.
Keywords: heart rate monitoring, wellness, neuromuscular efficiency, association football, heat training.